Even with new trends in search engine optimization, the statement that a picture says more than a million words applies. A single high-quality image can potentially bring life to a website’s content. In addition, a well-written HTML image title is a surefire way to improve the user experience.
But if you thought images were all about content and image matching, you might be surprised. With images, you can not only target web visitors but search engines as well. However, to get the full power of an image, you need to look a little under the hood and understand the HTML that displays images on your website.
After reviewing the components of an image tag, you can tweak the ones that will affect your search engine ranking. Usually, the target objects are the img src title and the HTML img alt title. Do you know the role these two play on your website? The answer will be the subject of this article.
Understand the image title and the image alt text
The easiest way to tell the difference between a title and alternate text is to look at an HTML image tag. Assuming your website is an online store that sells furniture, a sample rocking chair image tag might look like this:
<img src = ”brownrockingchair.jpg” alt = ”brown rocking chair on sale” title = ”brown rocking chair”>
In web design, the elements with an equal sign are given the name attributes. Note that the above example is only an illustration. In real applications, the attributes are much more and can include a class, an ID, height, width, and so on.
The tag makes it easy to identify the alternate text and title. You will find that the alt attribute is more informative when compared to the HTML cover photo tag. A look at the uses of both attributes reveals why this is so.
What is the image title used for?
The title appears when a user hovers over an image on your website. Therefore it will only be displayed after the images have been loaded. If a user sees the title, they have already viewed the image. As such, it doesn’t have to be very descriptive. For example:
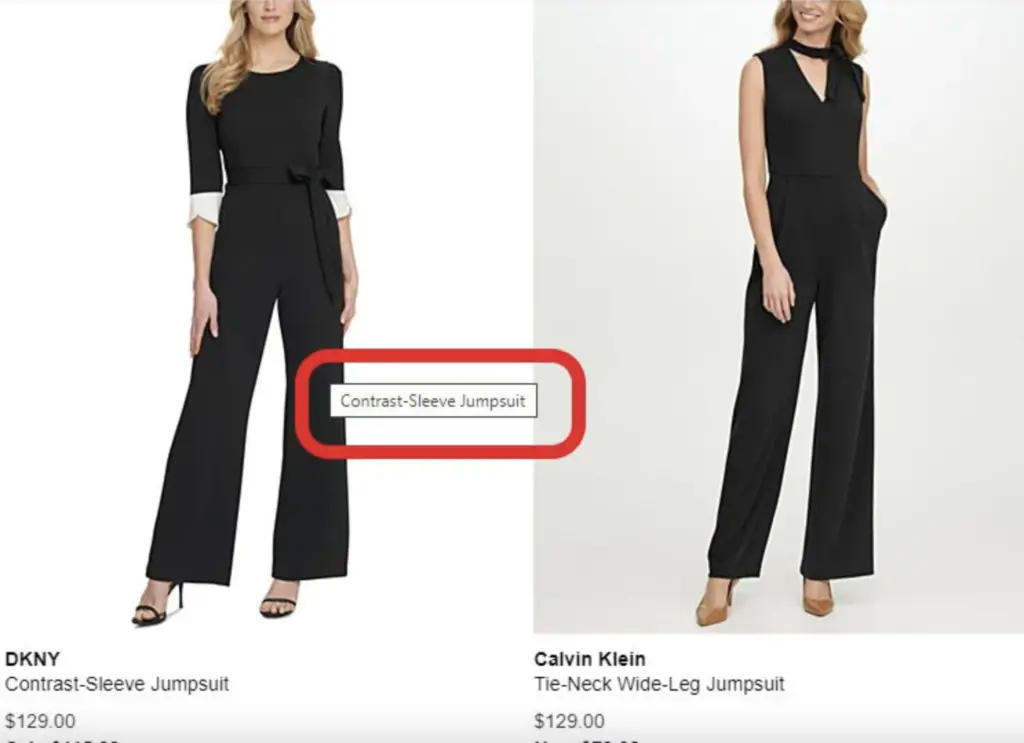
However, titles are very important when it comes to enhancing the user experience. Believe it or not, visitors may have trouble understanding why some images of your website appear in certain parts of your website. A title is useful for providing an answer.
Some browsers do not display the title when you hover over an image. However, since you never know what your visitors are using to navigate your website, it is better to include a title attribute in your image tag.
What is the alt text used for?
The alt text serves more than one purpose. You can break it down as follows:
The alt text is displayed every time an image cannot be loaded. Almost all browsers allow alternative descriptions to display empty images. This could be due to an incorrect image filename or a damaged URL. Poor internet connections can also prevent images from loading properly. In such a case, the picture alt title appears and explains everything about the picture to the visitor.
The alt text is also displayed when users turn off images. As much as images enhance web pages, some users prefer plain text versions. You can find out more about images by reading the alternative text.
Blind users will also benefit from well-written IMG-ALT titles. Screen readers use them to describe an image to visitors who cannot see it. In general, alternate texts will help make your website more accessible.
The importance of maximum accessibility is so great that the W3C actually advocates alternative texts. One line from their guidelines reads:
If you are using the img element, include a short text alternative with the alt attribute.
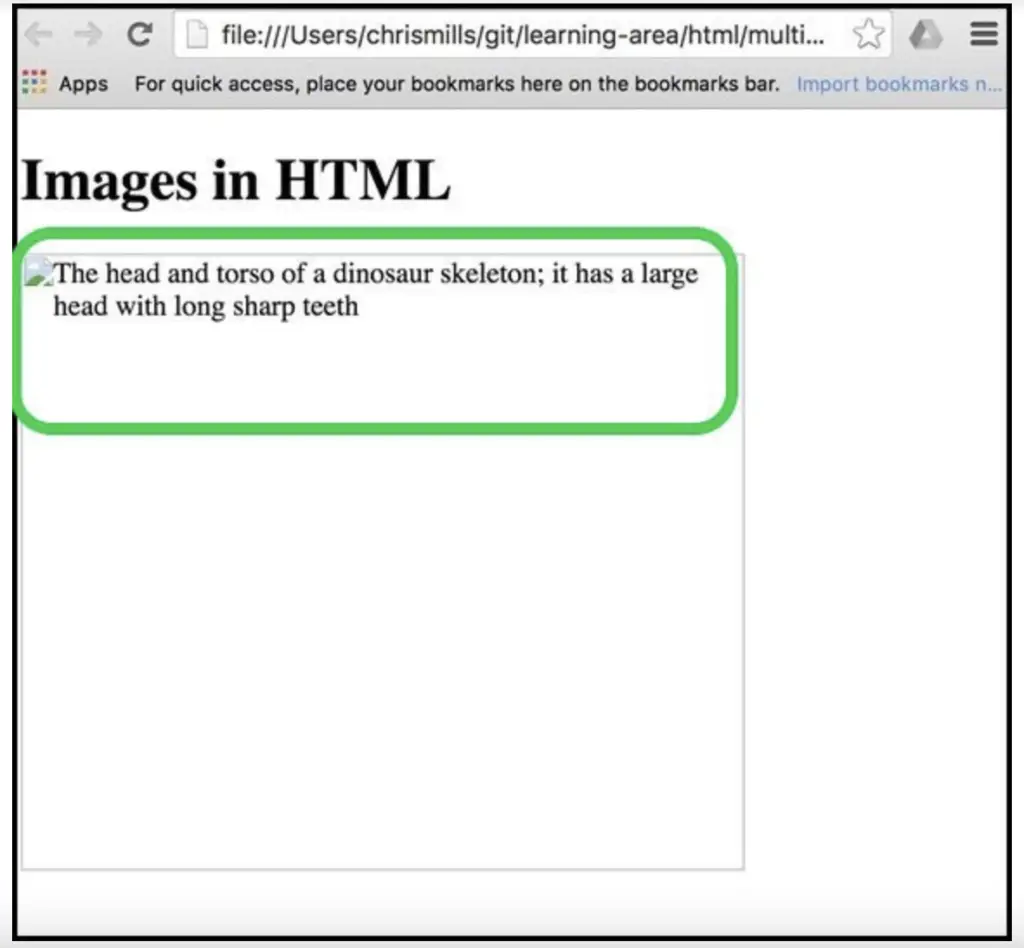
After all, search engines use alt text to better understand what an image is about. Therefore, alt text, just like other content on your website, is crawlable. The image below shows an example of alt text:
Which is more important: image title or alternative text?
It’s safe to call the alt attribute more important after looking at the usage lists of titles and alt texts. However, it would be a mistake to believe that titles are useless. The truth is, each point can matter depending on your goals.
If your main concern is improving the usability then your main focus should be on titles. As mentioned earlier, you can use titles to provide additional details about an image. As soon as a user hovers over it, the description should appear.
But why don’t search engines pay particular attention to image titles?
Well, the answer has a lot to do with search engine development. The developers wrote most of Google’s code base back in 1999. There were also significant additions over the next year. However, you have never considered unpopular and undiscovered HTML elements.
Since web designers didn’t use titles often, there was no need to provide them. Updates to the core code never made the HTML cover tag as important as other attributes.
When thinking about SEO, the alternative text you should focus on. Remember that Google treats the information in the alt attribute as normal webpage content. So it is indexed. In addition, search engines can have problems crawling an image. Alternate texts are a great way for you to know what an image is about.
In addition, alt texts take the accessibility of websites to a whole new level. Despite techniques like lazy loading, it is almost impossible to ensure that all of the images on your website are 100% loaded. A visitor can disable images or have a connection that is so slow that images never load. Armed with alt text, you can be sure that a user knows what an image is about, regardless of whether it is loaded or not.
In summary, the importance of alt text far exceeds the title attributes. Their uses are relatively numerous and their impact on the ranking of a website is remarkable. While tweaking both the title and alt text is important, it is good to give more weight to the information in the alt attribute.
Optimizing alt text for SEO
SEO is still one of the safest ways to organically generate quality traffic. While there are numerous ways to optimize a website, perfecting the alt text is ideal for setting up your website images for more traffic.
Write for people
When writing alternate text, the rule of thumb is, “Write like you’re writing for a blind person.” Given the occasions that alt text appears, it doesn’t hurt to keep the rule in mind at all times. As already mentioned, the information contained in the picture alt title is displayed when pictures cannot be displayed. So you want it to say all about the hidden image.
Therefore, write a statement that a person can read and understand. It is even more important to form a descriptive sentence. A blind person may be navigating your website and all you can see is what you type. The image below shows a good and bad example of alt text for the same image:

Write for search engines
Alt-text provides an image description not only for users but also for search engines. Therefore insert a keyword. Like other content, note that it contains a keyword that rhymes with the general flow of the web page the image is on.
Also, avoid bad SEO practices like keyword stuffing. Search engines mark your content as spam, which keeps your ranking low. It is better to write alt text poorly than to fill it with keywords. As a control, make sure that you do not use the keyword in more than 70% of your images.
Keep alt text short and sweet
The alt text describes an image, and it can be tempting to put many words in quotation marks around the alt attribute. But don’t do this. Search engines will not penalize you for this, but they will focus on the first sixteen words of the alternative description. 125 character alt text should adequately describe an image without compromising the usability.
However, if you think an image requires a long description, it is advisable to use the longdesc attribute. HTML4 and its successors allow this attribute in the image tag.
Alternate text examples
When you’re just starting out with SEO, understanding the difference between good alt text and poorly written alt text can be a little tricky. Therefore, it is useful to look at examples. To illustrate this, imagine a picture of a red, fast moving car on your website.
Your image tag might look something like this:
img src = ”speeding-car.jpg” alt = ”red car” title = ”auto”
In such a case, the alt text is not ideal. It gives very little information about the image. A better version may appear as:
img src = “speeding-car.jpg“ alt = “red car is racing on the motorway“ title = “Car“
If you know the name of the motorway, it can’t hurt to include it in the alt text. Avoid compromising your keywords or keyword stuffing at all costs. For example, if the keyword on your website is “red car,” leave a description like:
img src = “speeding-car.jpg“ alt = “This is a red car. The red car drives very fast and is such a beautiful red car“ title =“Car“
While the above description focuses solely on the image, keyword stuffing taints it. Search engines will disapprove of such spam phrases. The second sentence does not provide useful information about the image to the user. Accordingly, it is wise to exclude them.
How to add an alternative text
How you put alt text in the image tag depends on what you used to create a website. When you’ve written the website hardcode, it’s better to add the alternate attribute manually. For example:
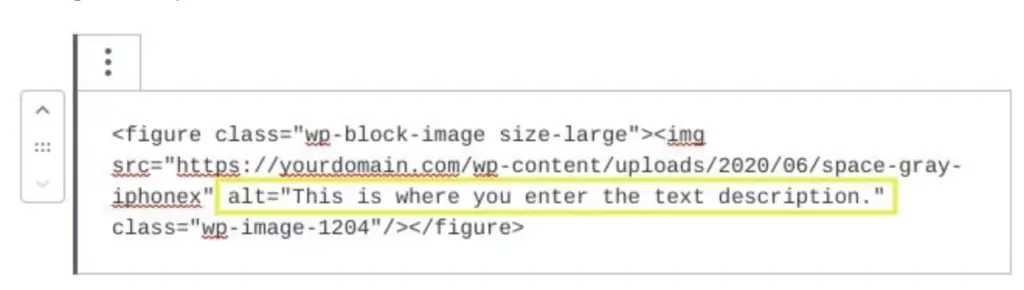
However, today’s web development hardly involves any hard coding. You may have used a content management system (CMS) or website builder. Be sure to find out what process your web design tool is using in adding all the text. Usually the methodology involves two or three steps.
In the world’s most popular CMS, WordPress, adding an HTML image alt title is a breeze. After logging into your account, find the image in question and click the “Edit” button. An input field appears that is ready to accept the data of the alternative attribute.
You can add alt texts to the WordPress media library. After selecting an image, find the alternative input field for the description that appears under the details of the image attachment. For example:
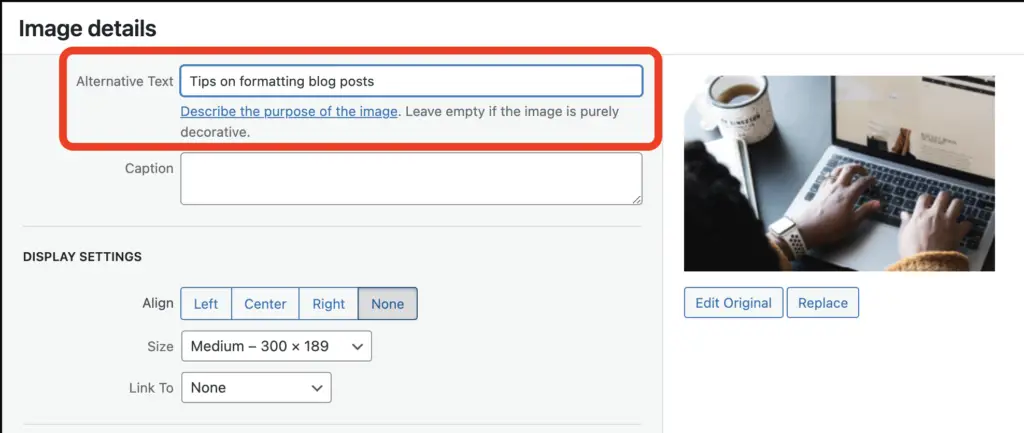
When the alt attribute should be left blank
Given the significant role alt attributes play in SEO, you may find it hard to believe that sometimes it is a good idea to leave them blank. Imagine a picture on a website for positional purposes only. The picture neither rhymes with the content nor does it enhance it. A web designer can only use such images to decorate a page.
Such design-only images can have a null alternative attribute. Describing them would be unwise as they do not add value to the available content. Screen readers will skip the images, which is fine as they won’t help the user understand the page better.
It’s also a good idea to exclude the alt text for images that contain words. All information is in the picture. A description of the words would therefore be irrelevant.
Optimize the image title
Since the title doesn’t affect the search ranking, there isn’t much you can do about it. In most cases it is shorter and less meaningful than the alternative text. Instead of giving more information about an image, a title gives it a name.
However, the W3C openly advocates including a title in an image tag. Your HTML may be W3C illegal if you do not title your images.
When writing the title, write text that is not only brief but also memorable. That said, single word titles are a no-go. A sentence that describes a picture and consists of no more than ten words should be enough.
Unlike the alt tag, which you can sometimes omit, there are no special occurrences that justify excluding image titles. Untitled images are only used to spoil the user experience. Hence, it is in the best interests of any SEO professional not to render a blank HTML cover photo tag.
Other alt image considerations
Undoubtedly, there is more to images than alternate text and titles. Optimizing the former and perfecting the latter is only part of the equation. To take full advantage of the impact of images on SEO, consider the following web image best practices:
Keep important text data away from pictures
It is better to write words than to draw them on a picture. Remember, search engines cannot thoroughly crawl an image or access words in an image. Avoid word-filled images unless HTML can’t output text data the way you want it, such as when writing complex chemical equations.
However, there is no harm in using images to represent graphics. HTML can provide the functionality, but images are a superior solution.
Pay attention to the context
The displayed image should harmonize with the information in a section. It would be a bad idea to include a car picture on a page that deals with outdoor apparel. At the same time, let your images be as original as possible. Search engines value original images because they value authentic content.
Write a good image file name
File names appear in the img src title attribute of the image tag. Search engines use it to learn more about the images on your website.
By default, images have alphanumeric filenames, such as:
A00002.jpg
Be sure to change the names to reflect the content of the picture. Remember to separate file names that exceed a word. A name like red-car-on-highyway.jpg would be difficult for search engines to read without the hyphens. However, do not change the image format, that is, letters after the period. Browsers can get confused when a format differs from the one specified by the filename.
Let your images make the SEO difference
When it comes to SEO, there is no argument that content is king. But images are just as much a part of the content of your website as words. By learning the art of perfecting the HTML image title and optimizing the HTML image alt title, you can use images to improve the ranking of your website.

